

X This displays the short names generated for non-8dot3 file names. TĜontrol what time field displayed or used for sorting Sĝisplays files in specified directory and all subdirectories. Rĝisplay alternate data streams of the file. P Pauses after each screenful of information. G Group directories first - Prefix to reverse order N New long list format where filenames are on the far right. D Same as wide but files are list sorted by column. Cĝisplay the thousand separator in file sizes. B Uses bare format (no heading information or summary). S System files I Not content indexed files H Hidden filesĚ Files ready for archiving Aĝisplays files with specified attributes. Specifies drive, directory, or files to list. Consider, for example, the DIR command: C:\>dir /?ĭisplays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory.ĭIR attributes]] If you use the modifier /? in a command, it will show the help command with all the switches available.
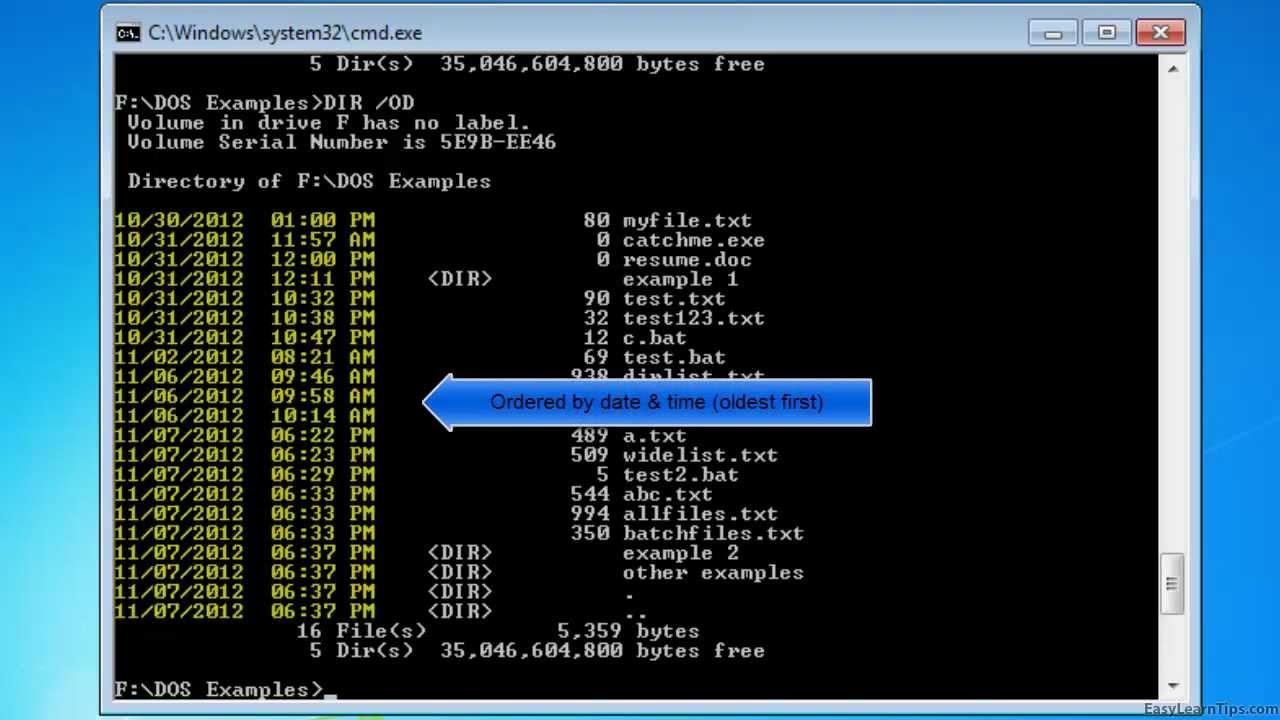
Switches allow you to modify the default operation of specific commands. Switches and parameters of a MS-DOS command Eg: dir *.txt will show us all the files with the extension txt Eg: dir edu.* will show us all the files with the name edu, regardless the extension. If we want to select all files with a certain extension or name, you can use the wildcard *.
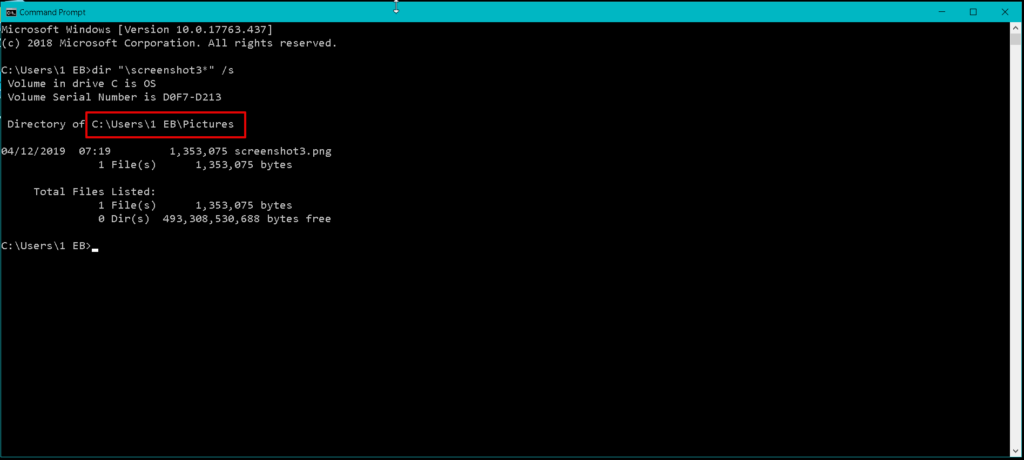
Eg: C:\>\windows\notepad.exe or C:\Windows>c:notepad.exe If we don´t specify the unit or directory: it will take the unit or the current directory, respectively. Only file name : this only works if we are on the same drive and directory where the file is. To refer to a file or directory we use :įull name : \ : this always works. When we see the word file in a help command, it usually refers either to a file or a directory. MS-DOS commands make little difference between a file and a directory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
